Four Stages of the Moon

The quarter of the aspect cycle that is waxing and still active, the new moon to the waxing half phase, is shown here with these two trigrams. In astrological aspects this represents the first quadrant. It covers from zero to ninety degrees waxing from the conjunction to the waxing square.

The quarter of the aspect cycle that is waxing and aware, from the waxing half moon to the full moon is shown here with these two trigrams. In astrological aspects this represents the second quadrant. It covers from ninety degrees to one hundred and eighty degrees waxing from the waxing square to the opposition.

The quarter of the aspect cycle that is waning and still aware, the full moon to the waning half moon is shown here with these two trigrams. In astrological aspects this represents the third quadrant. It covers from one hundred and eighty degrees to ninety degrees waning from the opposition to the waning square.
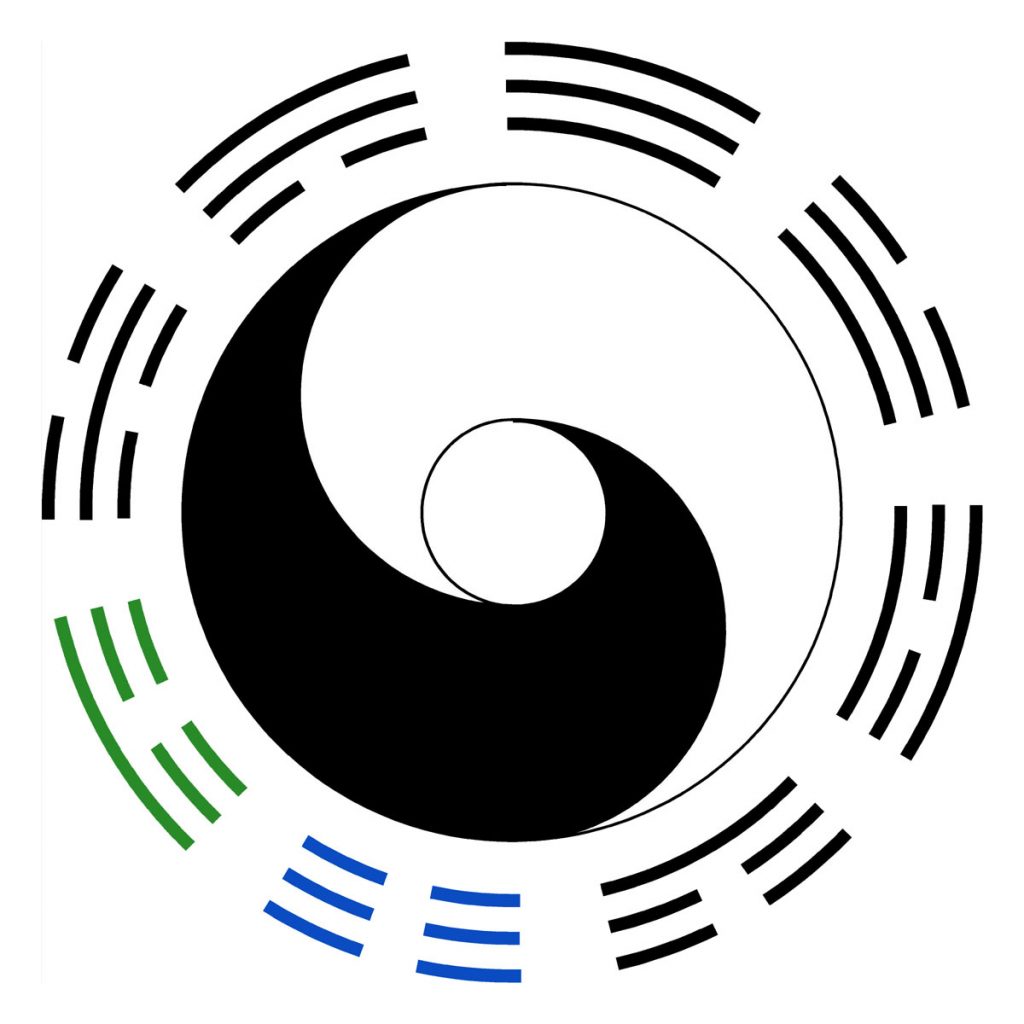
The quarter of the aspect cycle that is waning and active, the waning half moon to the new moon is shown here with these two trigrams. In astrological aspects this represents the fourth quadrant. It covers from ninety degrees waning to zero degrees (270 to 360), from the waning square to the conjunction.

Here we see the full cycle of the trigrams arranged around the wheel. The colours of the trigrams are presented in their correct positions and sequence for the cycle of the day. The greatest brightness is at the top for the full moon or opposition, and the greatest darkness is at the bottom for the new moon or conjunction. One can see the corresponding three solid lines for the greatest brightness, and the three broken lines for the greatest darkness. Actually the greatest brightness is the period leading right up to the full moon, but not a second after it. The greatest darkness is likewise the period leading up to the new moon but not a second after it.
